Academic pharmacist Nataly Martini discusses the medical management of asthma in adults and adolescents, which has evolved to prioritise early anti-inflammatory treatment. She also explains how to improve patient outcomes by proactively identifying poor asthma control and supporting equitable access to education and treatment
Management of diabetes webinar 2 - assessment answers
Management of diabetes webinar 2 - assessment answers
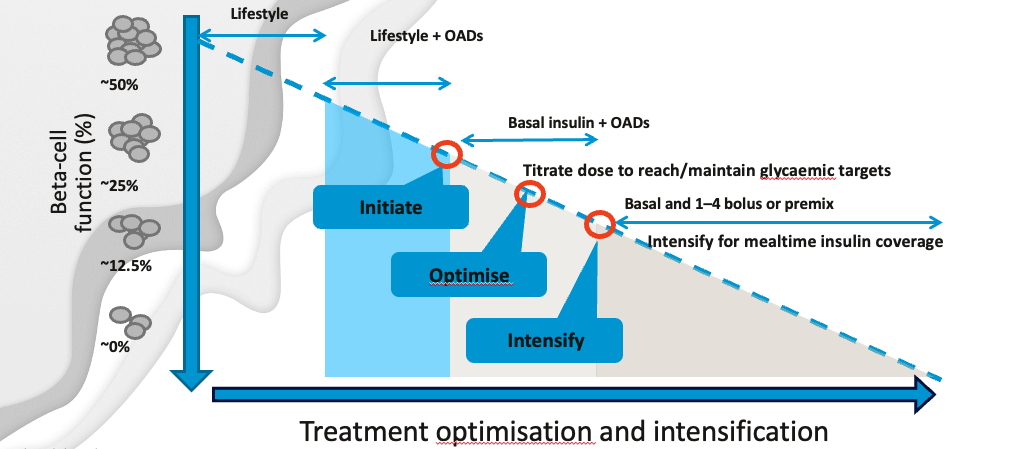
Below are the answers to the assessment from the webinar: Insulin therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes
Record your score in the Capture box at the bottom of the page for your own records.
1. What are TWO reasons why insulin is eventually required in many patients with type 2 diabetes?
a. At diagnosis, 50% of beta cell function is lost, and there is eventual loss of the majority of insulin producing capacity
d. Secondary failure of non-insulin therapies is common
2. What are TWO benefits of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes?
a. Insulin can be introduced at any stage of a patient’s type 2 diabetes trajectory
e. There is no maximal dose of insulin
3. Which TWO of the following statements regarding the initiation of insulin therapy are correct?
b. Insulin should be commenced if HbA1c remains above target despite optimising non-insulin therapies
c. It is important to exclude secondary causes of hyperglycaemia, such as sepsis, before starting insulin
4. Which TWO of the following statements regarding the early initiation of insulin therapy are correct?
a. Insulin should be initiated early to avoid patients spending time with damaging levels of hyperglycaemia
c. Insulin therapy is simpler and safer when initiated early
5. Which statement regarding the selection of insulin regimens is correct?
c. Insulin regimens should be individualised according to patient preferences, abilities and desires
6. When comparing basal insulin versus premix insulin, which TWO of the following are correct? For a given baseline HbA1c:
b. there are similar rates of hypoglycaemia with basal and premix insulins
d. there is similar glycaemic control with basal and premix insulins
7. What are FOUR possible options for intensifying insulin therapy?
a. Add doses of rapid-acting insulin to basal insulin or use multiple doses of premix insulin
c. Metabolic surgery for those who are highly insulin resistant
d. Reduce carbohydrate intake
f. Use non-insulin pharmacotherapy





